Writer: Sanna Peltonen, MUOVA, Pictures: Veera Hautala, MUOVA
SMEs need support from external organisations when they are developing eco-innovations. Intermediary organisations have an important role in encouraging, promoting, and facilitating business-to-business linkages and partnerships. Intermediary organisation can be public or private. They can be non-profit or for-profit organizations like chambers of commerce, trade associations, local and community groups; state and local governments, academic institutions, and private corporations (http://www.hjventures.com/SBA/Intermediary-Organization.html). Intermediary organisations are facilitating SMEs innovation activities by bringing together different organisations and knowledge that is needed for successful eco-innovation.
Intermediary organisation personas: Promoter, Networker and Dealer
Personas are fictional profiles, which summarizes the essential characteristics and highlights the shared interests of each actor. Personas are used in the service design to guide the development and to help in creating a good user experience for the target group.
In the Ecolabnet project, we conducted a survey for Intermediary organisations in six countries in the Baltic Sea region. Personas were created based on the survey data and they represent the roles and expertise that intermediary organisations see they have in supporting SME companies.
In the Ecolabnet project, personas are used when mapping out actors and their contribution to a network of service providers for eco-innovations.
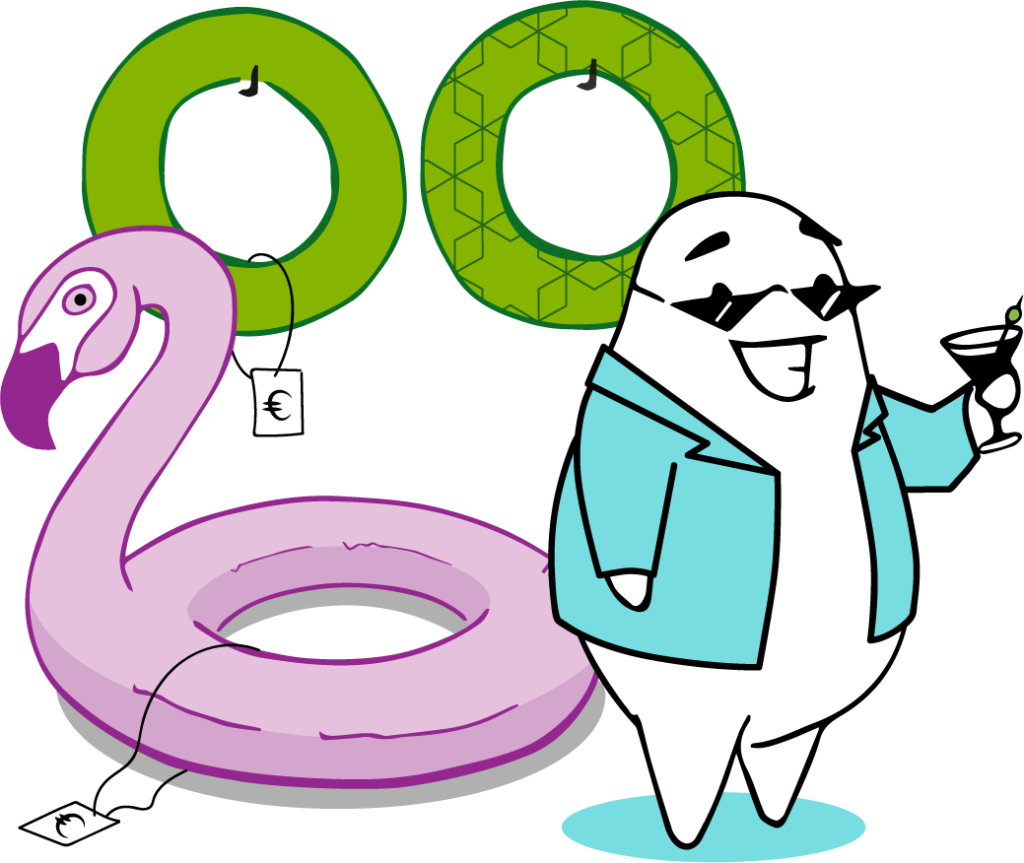
PROMOTER
”Commercialisation and branding? – We can help you with our business network!”
| Promoters see that their role is to focus on commercialisation, fostering networking and partnerships. They also value the branding and legitimation issues (e.g. creating distinct brand and social acceptance). Promoters’ main expertise areas relate to questions like – Potential business opportunities – To satisfy customer needs and – Differentiating from competitors. | Promoters main partners are – Commercial consultants – Universities and research institutions and – Regional business development organizations. |

NETWORKER
”Networking and information? – We support you also in eco-innovations.”
| Networkers see that their role is to focus on fostering networking and partnerships as well as information gathering and dissemination. Also forecasting and road mapping (e.g. providing avenues for firms in eco-innovation) are seen important. Networkers’ main expertise areas relate to questions like – Efficient use of resources, – Reduction of environmental impact on business operations, and – Cost reduction and – Potential business opportunities. | Networkers main partners are – Regional business development organizations, and – Universities and research institutions. |
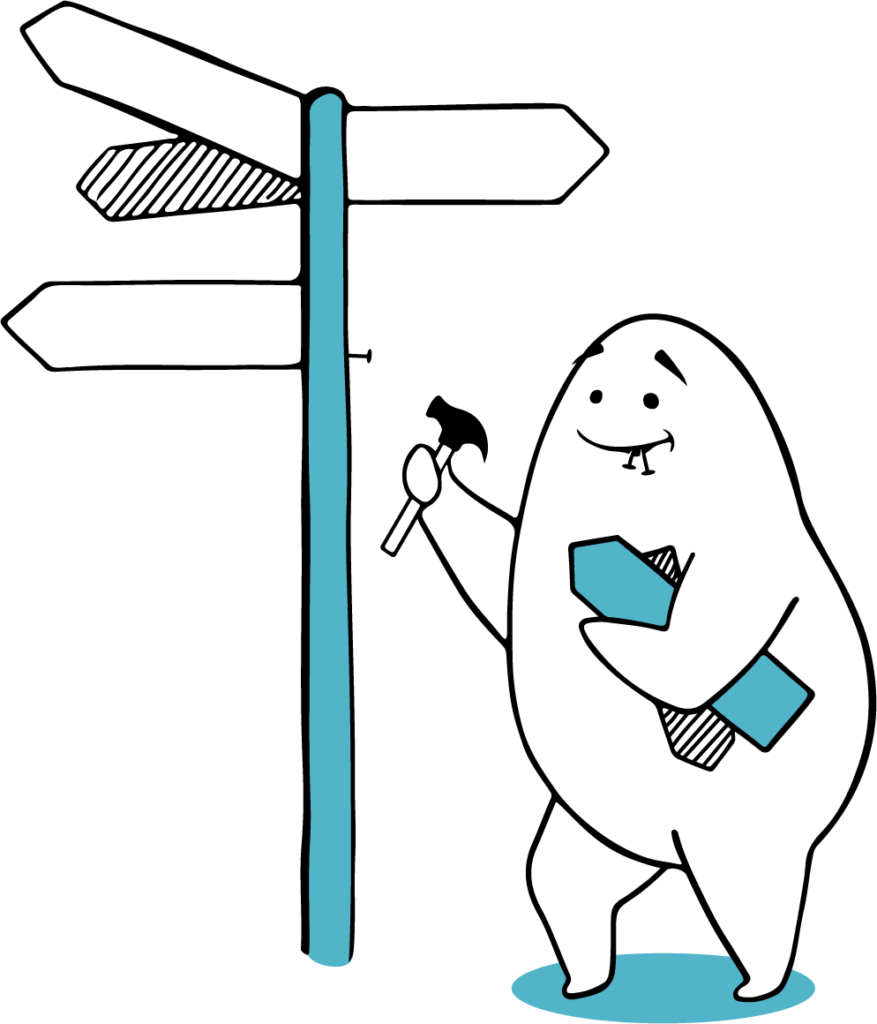
DEALER
”Developing eco-innovations? – We can provide you access to resources!”
| Dealers see that their role is to focus on providing access to financial, human and knowledge resources for eco-innovation. They also see that they have important role in commercialisation and fostering networking and partnerships. Dealers’ main expertise relate to questions like – To satisfy customer needs – Potential business opportunities – Meeting stakeholder expectations – Differentiating from competitors | Dealers’ main partners are – Universities and research institutions – Industry associations |
